 Applications
Applications
Our organisation categorises electrical components based on specific purposes and voltage criteria, simplifying their selection for diverse applications.
 What is an Energy Audit?
What is an Energy Audit?

An energy audit is a systematic, technical study of how energy is consumed in a facility,be it an industrial plant, commercial building, hospital, campus, or utility network. It tracks how energy enters the system (electricity, fuel, steam, compressed air), how it flows through equipment and processes, and where it is ultimately consumed or wasted.
Under India’s Energy Conservation Act, 2001 , an energy audit is defined as the verification, monitoring, and analysis of energy use, accompanied by a technical report that provides recommendations for improving energy efficiency, including a cost–benefit analysis and an actionable plan to reduce energy consumption.
 Objectives of an Energy Audit
Objectives of an Energy Audit

The primary aim of an energy audit is to improve energy performance while ensuring safety, quality, and productivity. Specifically, an energy audit helps to:
 Why is an Energy Audit Required?
Why is an Energy Audit Required?

Energy is often one of the top three operating costs in any facility, comparable to labor and raw material. Unlike labor or materials, energy costs can be reduced significantly without affecting output by improving efficiency.
An energy audit is essential because:
Electricity tariffs, fuel costs, and demand charges continue to rise, while governments push for reduced energy intensity and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Overheating cables, throttled valves, leaking compressed air, poor power factor, or harmonics rarely trigger alarms but waste significant energy over time.
Every unit of energy saved is equivalent to a unit that doesn’t need to be generated or purchased, often cheaper than adding new capacity.
Large “designated consumers” in India are required to conduct periodic energy audits. Demonstrating energy efficiency also strengthens ESG (Environment, Social, Governance) performance and corporate reputation.
 Who Needs an Energy Audit?
Who Needs an Energy Audit?

Energy audits are relevant for any organisation with significant energy consumption, including:
 When Should You Conduct an Energy Audit?
When Should You Conduct an Energy Audit?

Energy audits are applicable at various stages of a facility’s lifecycle:
For large or energy-intensive facilities, detailed audits ensure continuous improvement and identify new saving opportunities.
Pre-project audits help right-size new equipment (transformers, cables, chillers, compressors, pumps, DG sets), avoiding overdesign and energy waste.
Audits trace causes of sudden rises in bills, demand, or penalties due to low power factor, demand charges, or high TOD tariffs.
Nuisance tripping, overheating, flickering lights, motor failures, or breakdowns may be caused by poor power quality, unbalanced loads, or harmonics,issues a combined energy and power quality audit can detect.
Organisations working towards ISO 50001, green building ratings, ESG targets, or internal sustainability goals use audits as a baseline for decarbonisation and energy management roadmaps.
 Benefits of an Energy Audit
Benefits of an Energy Audit

A professionally executed energy audit delivers financial, operational, and environmental benefits:
Reduce electricity/fuel consumption, kVA demand, and improve power factor, often recovering audit and investment costs within months.
Efficient systems run cooler, reducing wear on transformers, motors, cables, and other equipment.
Optimised HVAC, lighting, and pumping improve production stability, product quality, and building comfort.
Correcting energy issues reduces breakdowns, trips, and maintenance costs.
Energy savings lower greenhouse gas emissions and help meet national energy efficiency goals.
Provides concrete numbers, baseline, savings potential, investments, and payback, making it easier to justify energy efficiency projects to management and investors.
 Standards and Guidelines Followed
Standards and Guidelines Followed

Our energy audits comply with national and international standards to ensure credibility and comparability:
Defines energy audit and empowers BEE to frame rules and guidelines.
Methodology for preliminary and detailed audits with sector-specific checklists and reporting formats.
International standard defining principles, roles, process requirements, and deliverables for energy audits.
Detailed guidance for building and process industry audits.
Energy Management System for continuous performance improvement.
IEC/IS standards, ASHRAE guidelines, OEM datasheets, and safety norms are referenced to ensure technically sound recommendations.
 Our Energy Audit Procedure
Our Energy Audit Procedure

We follow a structured, multi-stage process aligned with BEE methodology and ISO 50002 standards:
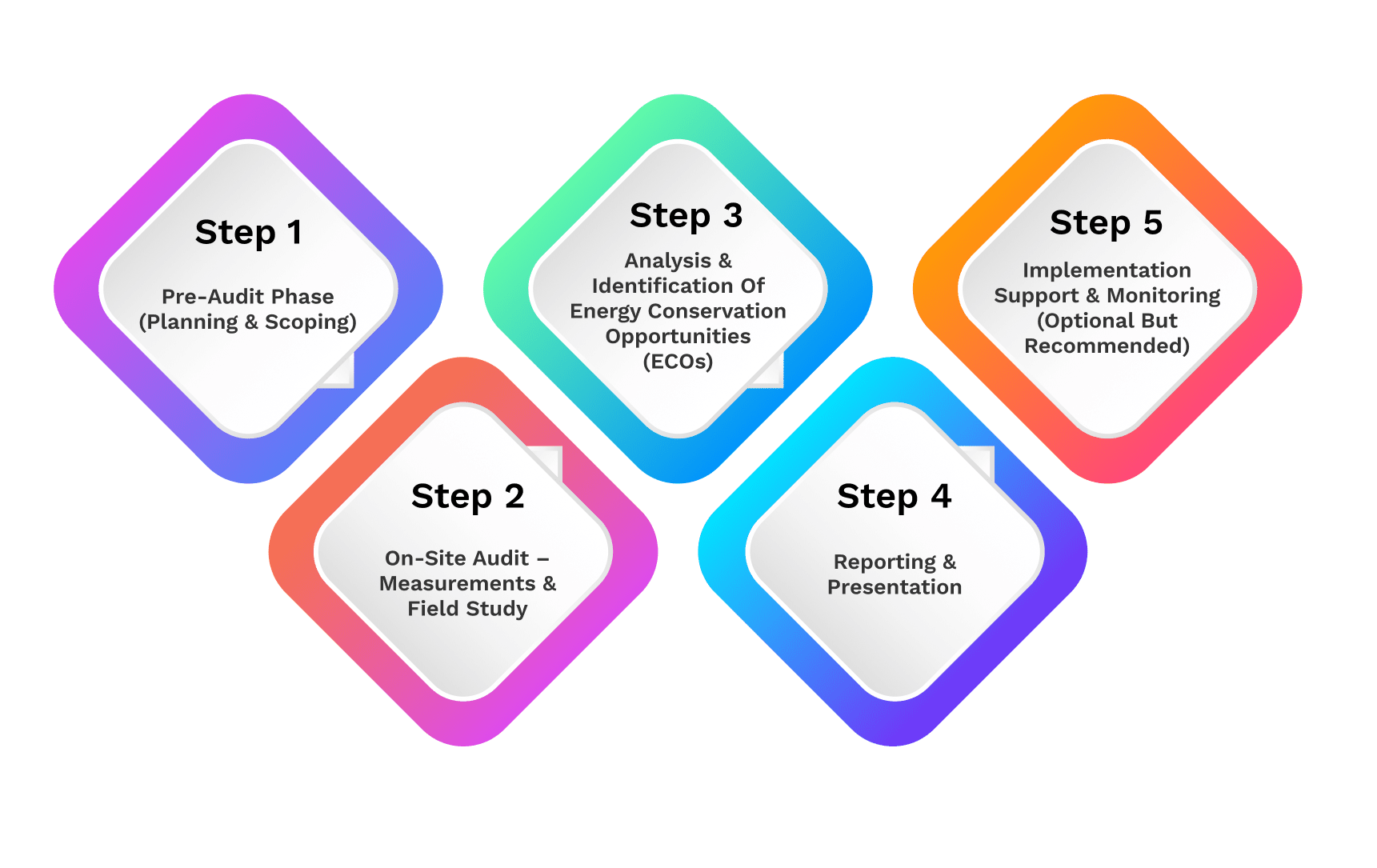
Visual inspection of transformers, switchgear, motors, drives, lighting, HVAC, compressors, boilers, steam systems, process equipment, and building envelope.
Voltage, current, power factor, harmonics, motor load, compressor performance, boiler efficiency, HVAC performance, lighting levels, and more under normal, peak, and part-load conditions.
Gather insights on real operating practices, constraints, and historical issues.
Deliver a comprehensive technical report including: