 Applications
Applications
Our organisation categorises electrical components based on specific purposes and voltage criteria, simplifying their selection for diverse applications.
 RUL (Remaining Useful Life) Study of Transformer, Motor & Cable
RUL (Remaining Useful Life) Study of Transformer, Motor & Cable

Remaining Useful Life (RUL) is the scientifically estimated time an electrical asset,such as a transformer, motor, or cable,can continue to operate safely and reliably before the risk of failure becomes unacceptable.
 What Is a RUL Study?
What Is a RUL Study?

A Remaining Useful Life (RUL) Study scientifically determines how long your electrical assets can continue to operate safely, reliably, and economically.
It combines:
We apply this methodology to three critical asset classes:
Focus on insulation system health (paper–oil), windings, core, bushings, tap-changers. We track moisture, dissolved gases, dielectric losses, hot spots, and mechanical integrity.
Focus on stator insulation, rotor bars, bearings, alignment, cooling, and power quality. We capture insulation indices, surge tests, vibration spectra, and thermal performance.
Focus on dielectric condition, water-treeing, semicon interfaces, joints/terminations, and sheath integrity using VLF–Tan δ–PD, IR/PI, and thermography.
 Why Is It Done?
Why Is It Done?

To understand the exact condition of critical equipment and prevent unexpected failures.
RUL Study helps identify:
 Objectives of the Study
Objectives of the Study

Establish the present technical condition via measurable indices (IR, PI, Tan δ, PD, DGA, vibration, thermography, etc.).
Use trends, aging models, and standards thresholds to forecast time-to-failure (technical or economic).
Thermal aging, moisture ingress, oxidation, mechanical loosening, harmonic stress, contamination, bearing wear, water-treeing, etc.
Replace periodic maintenance with data-driven interventions.
Prioritise repairs/replacements before failure to protect personnel and equipment.
Stage investments by risk criticality; extend life where feasible; avoid premature replacement.
 Why This Study Is Required
Why This Study Is Required

Insulation weakens rapidly with heat; even a 6–8°C rise can cut insulation life nearly in half.
Overvoltage events, switching surges, harmonics, and partial discharge accelerate dielectric breakdown.
Vibration, misalignment, dust, moisture, and corrosive surroundings contribute to faster deterioration.
Frequent starts, overloads, unbalanced loads, and poor power quality increase thermal and mechanical strain.
Issues like incipient PD, loose connections, early-stage bearing wear, and water-treeing often remain undetectable without specialised diagnostics.
Audits and insurers increasingly demand documented condition assessments for safety and reliability.
 Benefits
Benefits

Early detection of PD, moisture, loose windings, bearing faults, water-treeing.
Implement drying, reconditioning, re-insulation, bearing replacement, sealing, or PQ corrections.
Lower arc-flash risk, fewer emergency outages, better contingency planning.
Reduce losses, penalties, and nuisance tripping by correcting harmonics/unbalance/loose contacts.
Risk-ranked CAPEX roadmap; defer non-critical replacements; negotiate warranties/insurance with evidence.
Standards-aligned results for regulators, corporate audits, and insurers.
 Standards Followed -Practical Matrix (Indicative)
Standards Followed -Practical Matrix (Indicative)

IEC 60076, IEC 60422, IEEE C57.104, IEEE C57.152, IS 2026, IS 1866 Type & routine tests, condition assessment, oil maintenance, DGA limits & trending
IEC 60034, IEEE 112, IEEE 43, ISO 10816/20816, IS 12615 Performance, insulation testing, vibration severity, acceptance criteria
IEEE 400/400.2/400.3, IEC 60502-2, IEC 60270, IEC 60885-3, IS 7098 Field diagnostics, acceptance & maintenance tests, PD, Tan δ
IEC 61000, IEEE 519, ISO 18434, IEC 62446 PQ limits, THD guidance, thermal inspections
IS 5216, IS 3043, NFPA 70E, site safety codes Safe isolation, earthing, PPE, LOTO
Latest editions applied; acceptance bands aligned to OEM data, asset class, and criticality.
 RUL Study Procedure Complete Workflow
RUL Study Procedure Complete Workflow

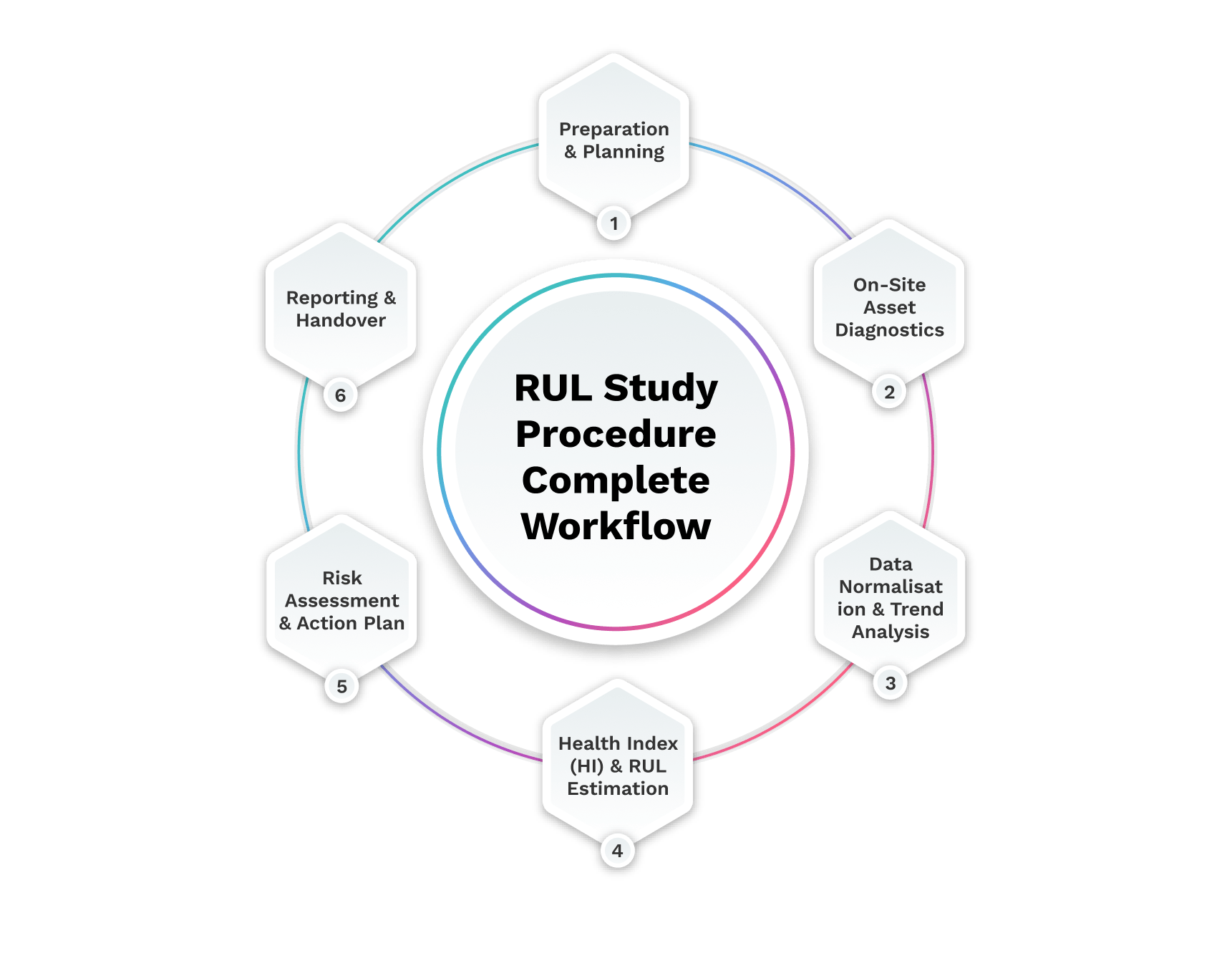
Immediate: Address severe PD/gas issues, dangerous vibration, and safety-critical defects.
Short Term (0–3 months): Dry-out, oil reclaim, bearing replacements, joint re-termination, PQ corrections..
Medium Term (3–12 months): Refurbishment, rewinding, or cable section replacement.
Plan Replacement: Budgeted replacement schedule with specifications.